The topics of carbon emissions and global warming have gained a good deal of attention in recent years, and coffee has an important part to play in the discussion. Greenhouse gases warm the Earth by absorbing energy and slowing the rate at which the energy escapes the planet, acting much like a blanket, insulating the Earth’s surface.
There are many causes that add to our changing climate, such as the burning of fossil fuels and other related human activities. Agricultural production alone accounts for approximately 10 to 12 percent of global greenhouse gas emissions. Such changes in the global climate are responsible for increased extreme weather patterns, drought, coral reef ecosystem collapse, and causing major shifts in agricultural land use, particularly within coffee producing areas.
Mitigating Carbon Through Trees
By the year 2050, research shows that half of the land used for specialty coffee will no longer be suitable for production. As global temperatures rise, current coffee varieties will be too slow to adapt to the rapidly changing temperatures, forcing coffee production to higher elevations to meet cooler climates. Unfortunately, less land is available at higher elevations and is often home to forested areas with vital watershed resources, increasing the rate of deforestation to further agricultural production.
Planting trees has been considered the most cost-effective and sustainable strategy to help combat and mitigate carbon emissions. Our forests capture and store carbon as well as provide ecosystem services such as soil nutrient cycling, wildlife habitat, and buffering against extreme temperature and weather events.
The Arbor Day Foundation recognizes the importance of tree planting as a useful tool to help mitigate the effects within coffee production and has taken major steps towards developing a program that allows everyone to easily participate in climate mitigation strategies through the purchase of Arbor Day Coffee. Funds from each sale of Arbor Day Coffee goes directly to tree planting projects around the globe. Each tree planted helps sequester carbon, playing an important role in reducing the overall carbon footprint of coffee.
Read: Back to the Roots: History of Arbor Day Coffee
The Biggest Culprits of Carbon Emissions in Coffee
How is the total carbon footprint of coffee from field to cup calculated? This process is a complicated calculation to perform because of the many variables of each unique situation. For the sake of simplicity, research has shown an average of 11 pounds of carbon dioxide (CO2e) emitted into the atmosphere for each pound of roasted coffee, which includes all activities from the coffee field to your brewed coffee cup at home.
The following diagram shows the distribution of the carbon footprint throughout the coffee supply chain, with 45 percent of the total footprint contributed by coffee consumption, whereas 31 percent is produced at the farm and central mill.
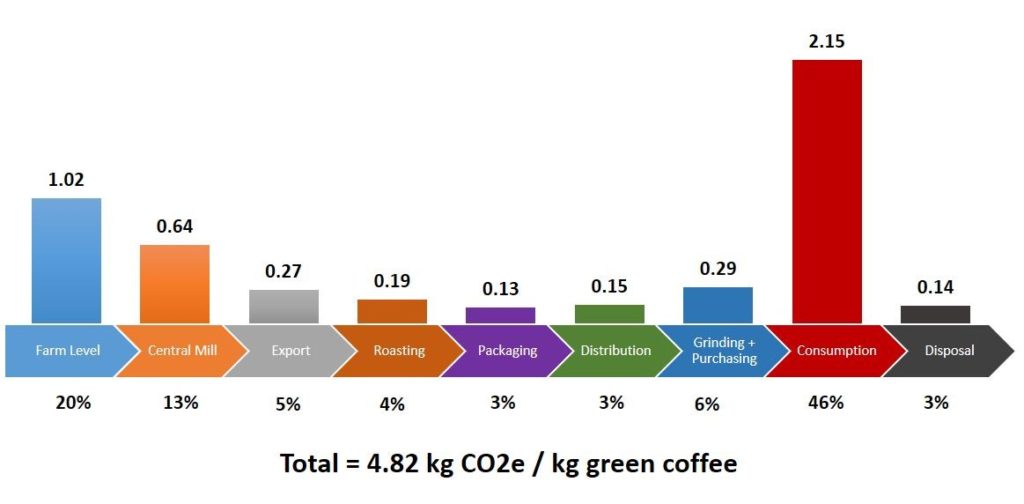
Measuring carbon footprints in the coffee supply chain has helped measure our environmental impact and provide an opportunity for consumers to invest in reducing their coffee carbon footprint through tree planting investments in Arbor Day Coffee.
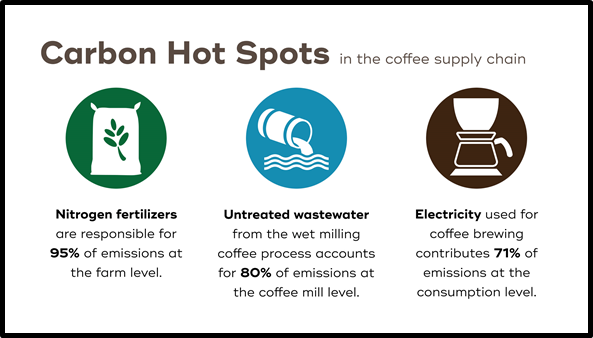
With your help, we can continue to support and maintain the planting of trees to provide benefits to coffee farmers, to help increase soil health, improve biodiversity and wildlife habitat, buffer against extreme weather conditions, and improve water resources and watershed management practices.
Learn more about Arbor Day Coffee here.


No Comments